Hello, World!
Welcome to CSE 230!
Principles of Programming Languages
Name this Computer Scientist (1)

Edsger Dijkstra “On the foolishness of natural language programming”, 1978

From one gut feeling I derive much consolation: I suspect that machines to be programmed in our native tongues — be it Dutch, English, American, French, German, or Swahili— are as damned difficult to make as they would be to use.
Fifty years later …

… Won’t LLMs like ChatGPT, Claude, Grok, … let us vibe code all the programs?
… why bother with Programming Languages?
Computation is specified by Programming Languages
Increased dependence implies increased need for getting code right
Safety Will this code crash?
Security Will this code broadcast my social security number?
Performance Will this code run in the appropriate time/space constraints?
Name this Computer Scientist (2)

Sir Tony Hoare

There are two ways of constructing a software design: One way is to make it so simple that there are obviously no deficiencies, and the other way is to make it so complicated that there are no obvious deficiencies.
How to ensure obviously no deficiencies ?
How to ensure obviously no deficiencies ?

The virtue of formal texts is that their manipulations, in order to be legitimate, need to satisfy only a few simple rules; they are, when you come to think of it, an amazingly effective tool for ruling out all sorts of nonsense that, when we use our native tongues, are almost impossible to avoid.
Name this Computer Scientist (3)

Greg Brockman, President, CTO & Co-Founder, OpenAI
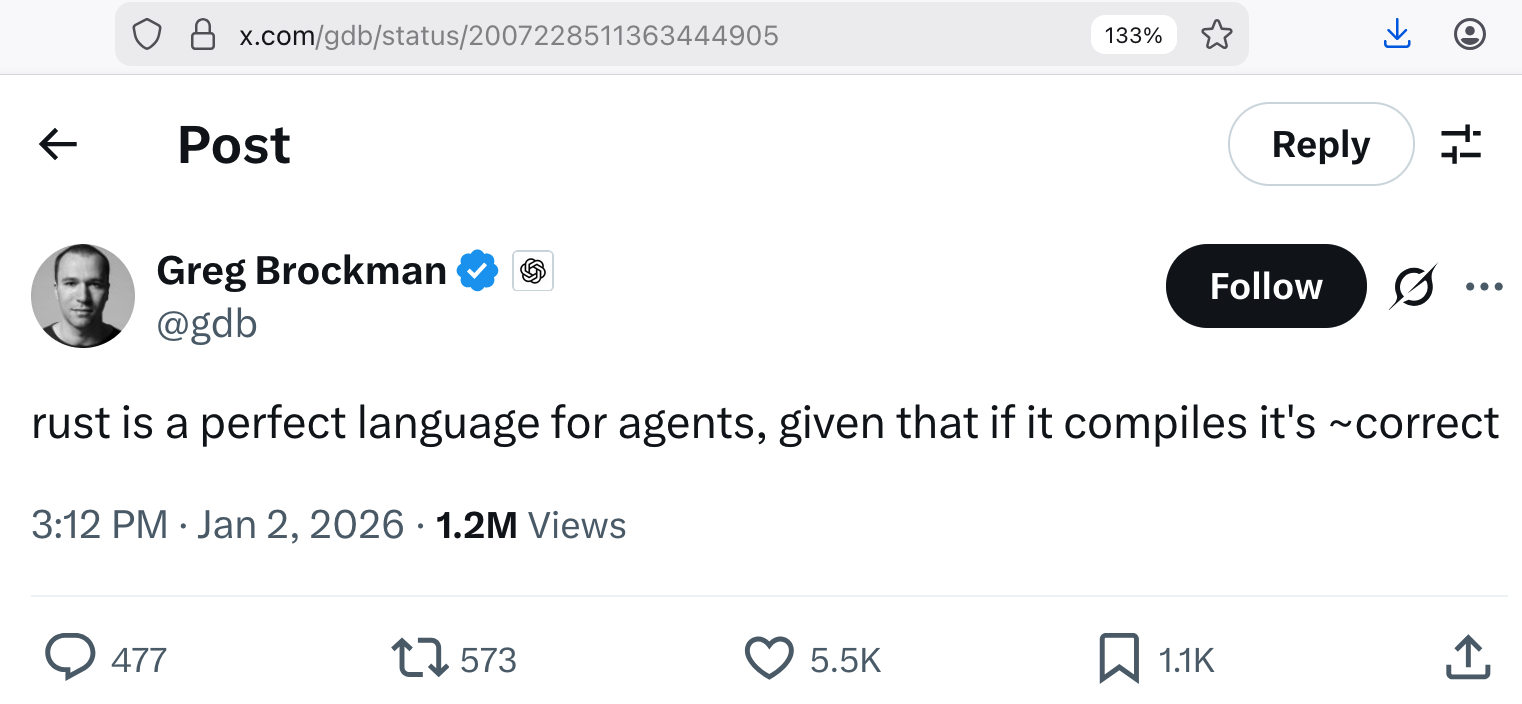
Not just OpenAI…
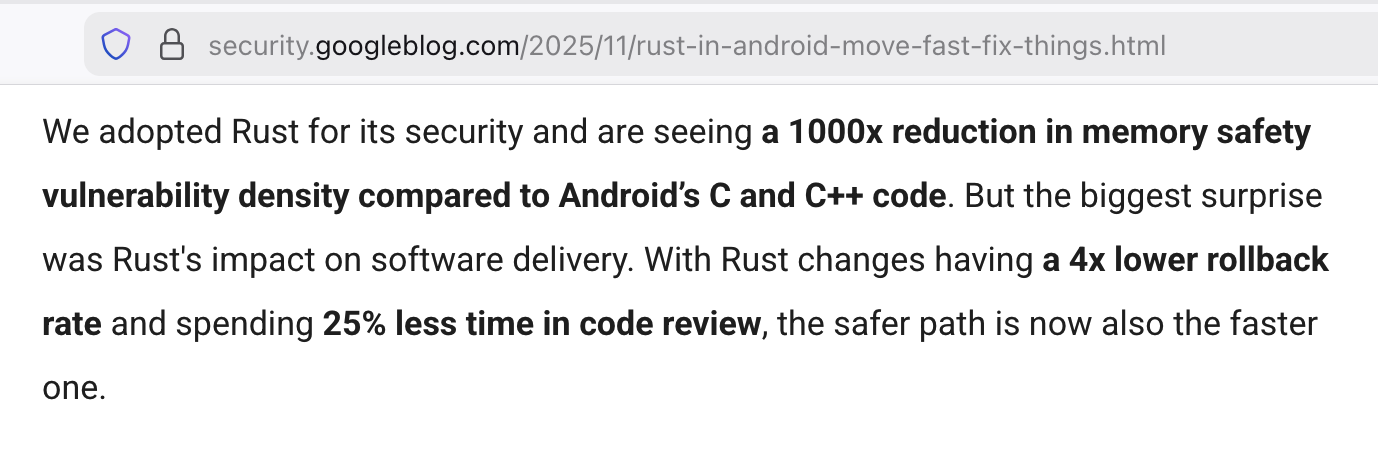
… similar stories from Microsoft, Meta, Amazon, etc.
Learning Goals for CSE 230
Abstraction: Intellectual and Algorithmic tools for reasoning about program behavior
How to specify what a program does?
How to be sure of what a program does not?
How to ensure “if it compiles, it is ~correct”?
Back to Esger Dijkstra…

“The purpose of abstraction is not to be vague, but to create a new semantic level in which one can be absolutely precise.”
Course Outline
Part I: Abstraction Foundations in Haskell
How to create abstractions via types and equational reasoning
- Algebraic Data & Functions
- Type classes
- Effects via Monads and Transformers
Part II: Zero-Cost Abstractions in Rust
How to enable zero-cost abstractions via ownership
- Effects via Ownership & Borrowing
- “Fearless” Parallelism & Concurrency
- Property based Testing & Verification
Logistics!
Course Staff
Instructor
Teaching Assistants
Policies
No podcasting.
No screens (phones, laptops) in lecture.
Yes attendance & class participation (worksheets).
Yes exams must be done at allotted time and location.
Yes you may use AI tools for assignments …
Grading
Class participation/worksheets (20%)
Programming Assignments x 4 (20%)
Midterms x 2 (40%)
Project (20%)
Class participation (20%)
“In class” worksheets handed out each lecture
Handed in at the end of the lecture
Turn in 75% of the worksheets to get full credit
Responses will be graded on participation (not correctness)
Programming Assignments (20%)
Four assignments released online
At least a week before due date
Via github classroom + codespaces
Submitted individually via github
Ok to discuss with classmates, but solution must be your own
Four late days used as whole unit
AI use is ok … but …
Midterms x 2 (40%)
Must be done at allotted time and location,
Two midterms (each 20%)
Closed-book, pencil-and-paper midterm exams,
During lecture on Th 2/5 and Tu 3/10 respectively
May use a letter-sized “notes sheet” of paper
Will heavily test understanding of assignments…
Project (20%)
Implement a concurrent, real-time, multiplayer game
Using
tokio+ratatui(terminal UI library)In a group of 2-3, in the second half of the quarter.
Evaluated with live demo and Q&A …
… during the final exam block on Thu 03/19 8:00a – 11:00a.
